MCP Nodes
Latenode MCP server allows external AI systems (AI agents) to run your scenarios as tools. Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a communication standard between AI systems and external systems, enabling them to interact by defining endpoints and providing authentication.
With Latenode MCP, you can expose your scenarios to AI clients like Claude Desktop, Cursor, or any MCP-compatible application.
MCP Trigger
MCP Trigger turns your scenario into an MCP server. Each node connected directly to MCP Trigger becomes a separate tool that AI clients can discover and call.

Server settings
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server Description | Description of your MCP server for AI context |
| Server URL | Copy this URL to use in your MCP client. |
| Version | Version identifier (any text, e.g., 1.0) |
| Authentication | Enable to require API Key for access |
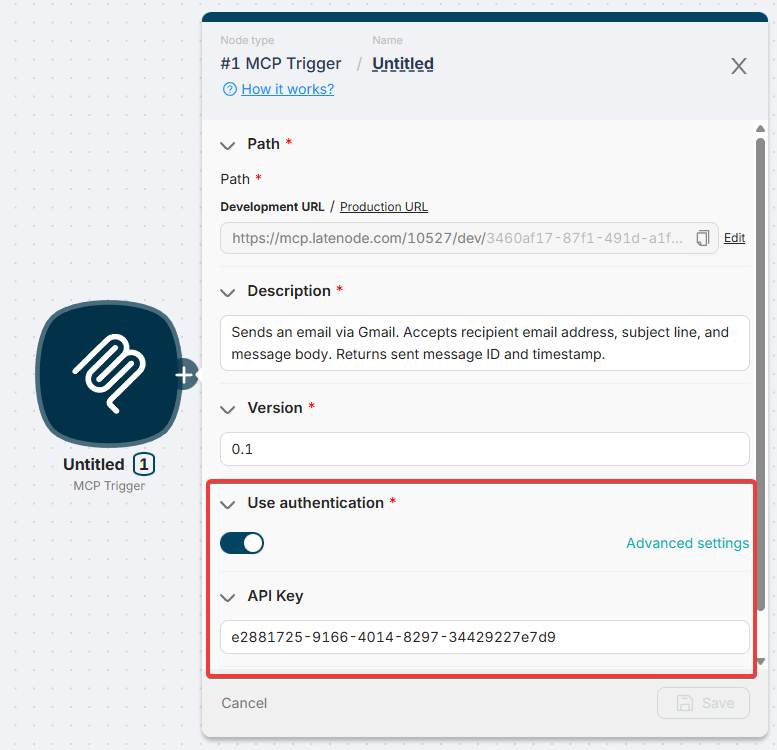
Tool configuration
Each node connected to MCP Trigger becomes a tool. Configure it in the first connected node's settings:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Tool Name | Required. Unique tool identifier (e.g., create_lead, send_email) |
| Tool Description | Description helping AI understand when to use this tool |

⚠️ Important: Without Tool Name, the tool won't be visible to AI clients.
Input parameters
Parameters define what data AI will pass when calling the tool.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Key | Parameter name (e.g., email, user_name) |
| Type | Select fromMCP for AI-fillable parameters |
| Description | Explanation for AI — what data to pass |
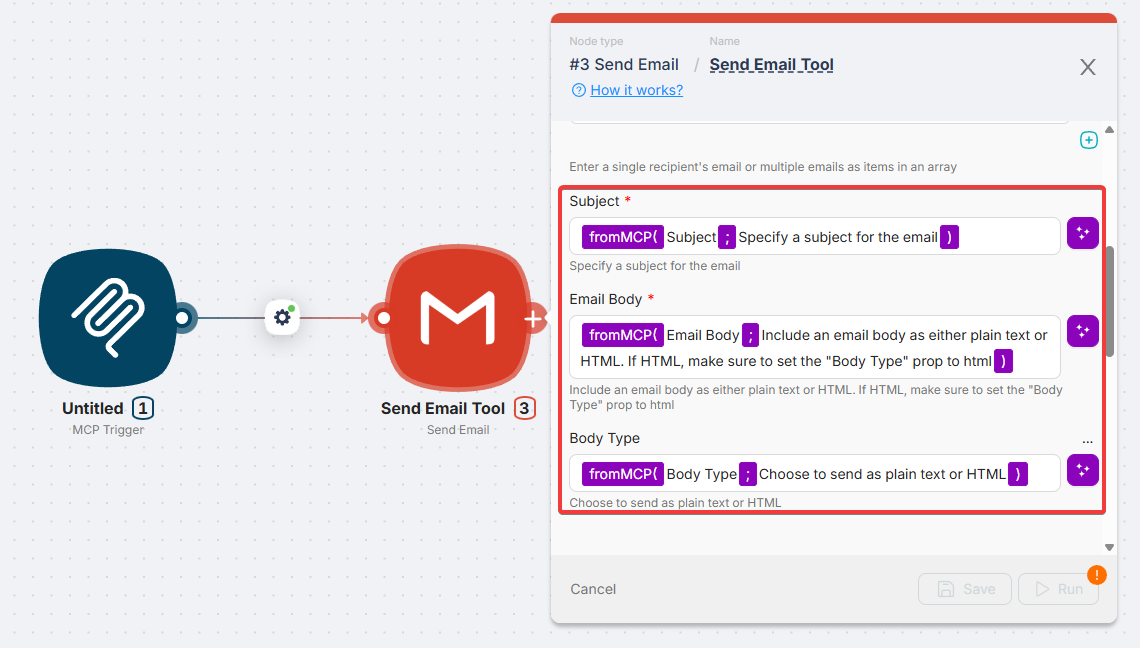
Example — lead creation tool parameters:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | fromMCP | Contact name |
| fromMCP | Contact email address | |
| phone | fromMCP | Phone number (optional) |
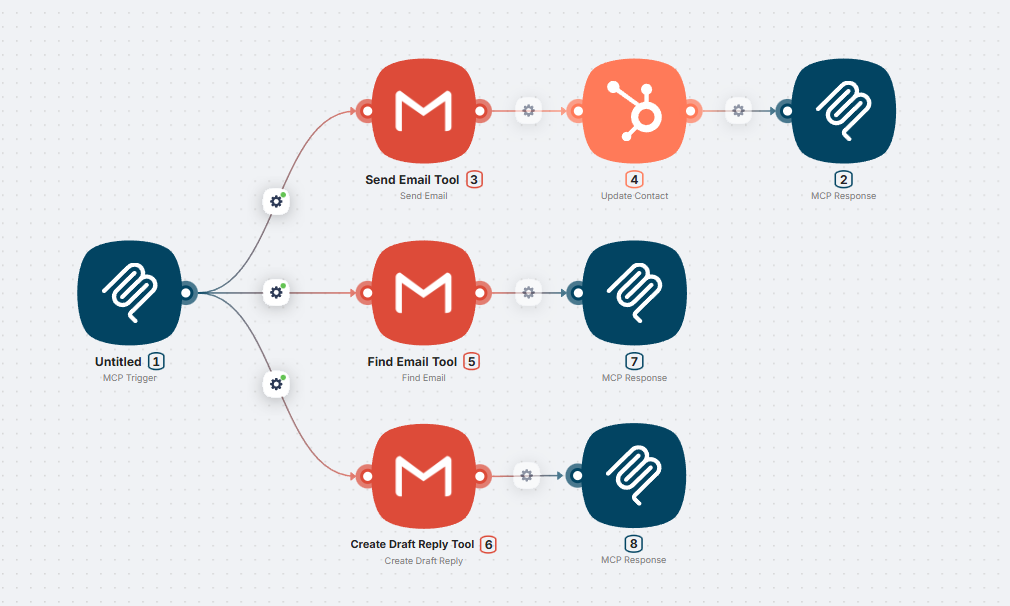
Multiple tools
You can create unlimited tools in one MCP server by connecting multiple branches to MCP Trigger.
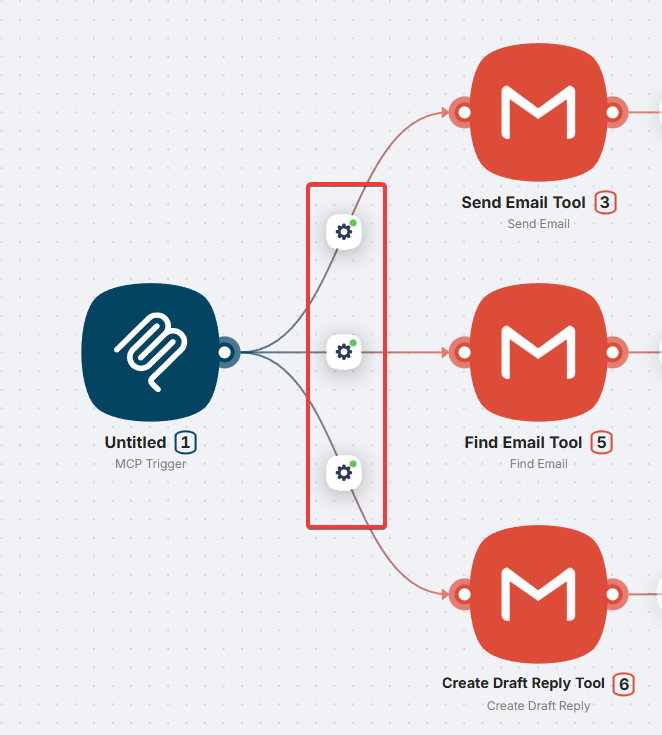
Each branch:
- Has its own Tool Name and Description
- Can contain any number of nodes
- Can use conditions, loops, AI agents, and any other Latenode nodes
- Operates independently
Automatic routing
When connecting nodes to MCP Trigger, a route filter is created automatically. This filter routes requests to the correct tool branch.

ℹ️ The filter is auto-generated and non-editable.
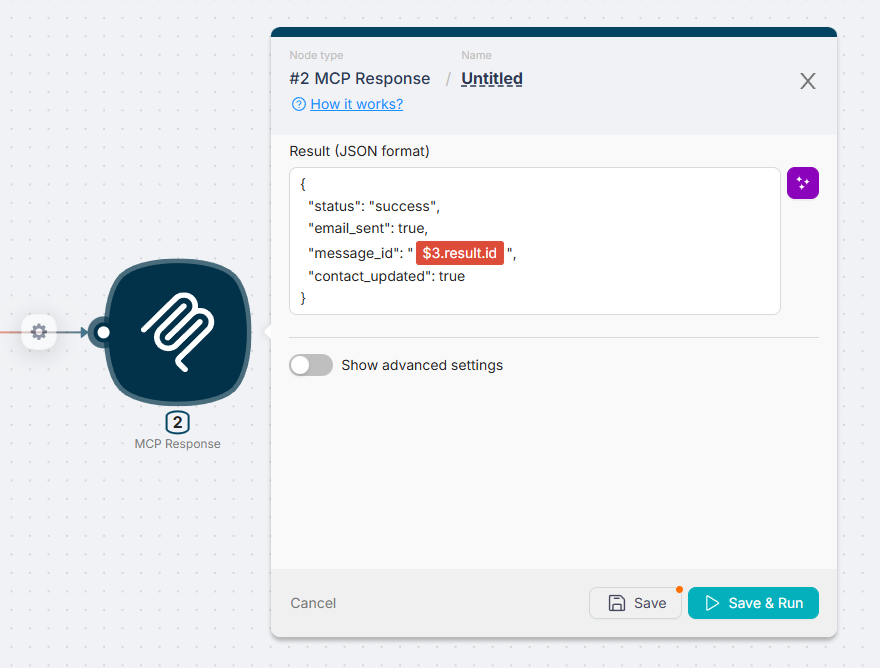
MCP Response
By default, the output of the last node in the tool chain is returned to the AI client. This often includes unnecessary data like headers or status codes.
MCP Response lets you specify exactly what data to return.

When to use
- Return only specific fields (e.g., just
bodyfrom HTTP response) - Create a custom response structure
- Hide technical details from AI
Configuration
Specify the data to return using variables from previous nodes.
Example: Simple Echo Tool
Step 1: Add MCP Trigger
- Create a new scenario
- Add MCP Trigger node
- Set Server Description:
Test MCP server
Step 2: Configure Tool
- Connect a Code node to MCP Trigger
- Set Tool Name:
echo - Set Tool Description:
Returns the provided text. Use for testing. - Add parameter:
- Key:
message - Type:
fromMCP - Description:
Text to return
- Key:
Step 3: Return Result
In the Code node:
return {
result: msg.message
}Step 4: Deploy
- Save the scenario
- Copy URL from MCP Trigger
- Connect to your MCP client
Best practices
Descriptions
Write clear descriptions so AI understands when and how to use your tools.
✅ Good:
Creates a task in Asana. Accepts task title and optional deadline.
Returns created task ID and link.❌ Bad:
Creates taskParameters
- Use descriptive names (
user_emailnotparam1) - Specify expected format in description (
Date in YYYY-MM-DD format) - Mark optional parameters
Response data
- Return only necessary data via MCP Response
- Avoid exposing technical details
- Structure responses for AI readability
Limitations
- MCP uses SSE (Server-Sent Events) — requires stable connection
- Tool execution time is limited by scenario timeout
- Binary data (files, images) requires additional handling